We note that there are point, x1 and x2 with x1 ≠ x2 and f (x1) = f (x2), for instance, if we take x1 = 2 and x2 = 1/2, then we have f (x1) =2/5 and f (x2) =2/5 but 2 ≠ 1/2 Hence f is not oneone Also, f is not onto for if so then for 1∈R ∃ x ∈ R such that f (x) = 1 which gives x/ (x21) =1The function f R → R defined by f(x) = 2x 1 is surjective (and even bijective), because for every real number y, we have an x such that f(x) = y such an appropriate x is (y − 1)/2 The function f R → R defined by f(x) = x 3 − 3x is surjective, because the preimage of any real number y is the solution set of the cubic polynomialIs x^3 x onetoone and onto?

Pdf 01 Sets Relations And Functions Himanshu Gautam Academia Edu
F(x)=(x-1)(x-2)(x-3) is one one or onto
F(x)=(x-1)(x-2)(x-3) is one one or onto-Q Consider the following x² 1, f(x) 5x 1, x > 0 Sketch the graph of the function 10H A Use online graphing calculator and sketch the graph of the function as follows From the above grapOnto function "every y in Y is f (x) for some x in X (surjective f "covers" Y) Notice that all one to one and onto functions are still functions, and there are many functions that are not one to one, not onto, or not either Not 11 or onto fX>Y, X, Y are all the real numbers R "f (x) = x^2"
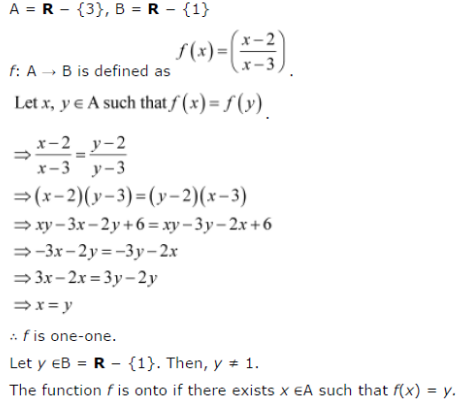



Let A R 3 And B R 1 Consider The Function F A B Defined By B Defined By Cbse Class 12 Maths Learn Cbse Forum
We have f R → R,f(x) = cos x Let f(x 1) = f(x 2) ⇒ cos x 1 = cos x 2 ⇒ x 1 = 2nπ ± x 2, n∈Z Above equation has infinite solutions for x 1 and x 2 Thus f(x) is many one function Also range of cos x is 1,1, which is subset is given codomain R Hence function is not onto 1 Let f(x) = x2 – 9, g(x) = 2x, and h(x) = x – 3 Find the solution to the following function (f)(1) (gh) 2 Solve the equation 5x2 56x36x 3 Let f(x) = x2 – 9, g(x) = 2x Find (f o g)(2) 4 read moreWeekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelled
The definition of a one to one function can be written algebraically as follows Let x1 and x2 be any elements of D A function f (x) is onetoone if x 1 is not equal to x 2 then f (x 1) is not equal to f (x 2 ) Using the contrapositive to the above A function f (x) is onetoone if f (x 1) = f (x 2) then x 1 = x 23 x2 2 >1 This shows that f(x) = x3 is not uniformly continuous on R 445 Let M 1;3) If x and y are in X, then f (x
Write the linear factorization of f(x)=x^4 2x^3 2x 1 Find the intervals in which the following function are increasing or decreasing f(x)=106x2x^2 f(x=> x = y ∴ f is a oneone function It is clear that f −1, 1 → Range f is onto ∴ f −1, 1 → Range f is oneone and onto and therefore, the inverse of the function f −1, 1 → Range f exists Let g Range f → −1, 1 be the inverse of f Let y be an arbitrary element of range f Since f −1, 1 → Range f is ontoGenerally, to differentiate a product function, the formula is as follows f(x) = g(x) * h(x) Where the derivative is f'(x) = g'(x)*h(x) h'(x)*g(x) In your example, this follows the general formula of product rule however, there is one extra term To make up for this, we have to alter the general formula slightly You now have to compensate for the third term




Ncert Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Relations And Functions Avail Free Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcq3k4crna5aowbckdwotcepc7srb Ubkhdcqsvwzwhqp8plminb Usqp Cau
The function fR>R f(x)=(x1)(x2)(x3) check if it is one one ,onto or bijection The solution is onto given in the graphIn mathematics, an injective function (also known as injection, or onetoone function) is a function f that maps distinct elements to distinct elements;F(x) = x 3 3 x 2 2 , a one to one function?



How To Prove That F X X Sqrt X 2 1 Is Injective Quora




Functions Discrete Structure L62 Functions Basic Terms Def A Function F A B Is Given By A Domain Set A A Codomain Set B And A Rule Which For Ppt Download
Precalculus Graph f (x)=2 (x1)^2 (x3) (x2)^3 f (x) = −2(x − 1)2 (x − 3) (x − 2)3 f ( x) = 2 ( x 1) 2 ( x 3) ( x 2) 3 Find the point at x = −2 x = 2 Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with − 2 2 in the expressionSolution to Question 3 A graph and the horizontal line test can help to answer the above question Since a horizontal line cuts the graph of f at 3 different points, that means that they are at least 3 different inputs x1, x2 and x3 with the same output Y and therefore f is not a one to oneLet y is in the co domain (Q) such that f(x) = y ⇒ 9x 2 6x 5 = y ⇒ 9x 2 6x = y 5 ⇒ 9x 2 6x 1 = y 6 (Adding 1 on both sides ) ⇒ (3x 1) 2 = y 6 ⇒ `3x 1 = sqrt(y 6)` ⇒ `3x = sqrt (y 6) 1` ⇒ `x = (sqrt (y 6)1)/3 in R^` (domain) f is onto So, f is a bijection and hence, it is invertible Finding `f^1` Let f−




Maths Important Questions For 18




11 The Function F R Rightarrow R Defined As N F X X 1 X 2 X 3
So, f is oneone function Clearly, f (x) = x2 x1≥ 3 for all x ∈ N So, f (x) does not assume values 1 and 2 ∴ f is not an onto functionSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreEquations Tiger shows you, step by step, how to Isolate x (Or y or z) in a formula f(x)=1/2x^3x and Solve Your Equation Tiger Algebra Solver Solution is x = 0 Solving a Single Variable Equation 74 Solve 2fx 2 2 = 0 In this type of equations, having more than one variable (unknown), you have to specify for which variable you want




Q17 Show That The Function F N N Given By F 1 F 2 1 And F X X 1 For Every X Gt 2 Brainly In
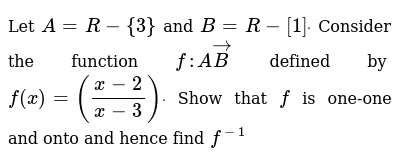



Let A R 3 And B R 1 Dot Consider The Function F Avecb Defined By F X X 2 X 3 Dot Show That F Is One One And Onto And Hence Find F 1
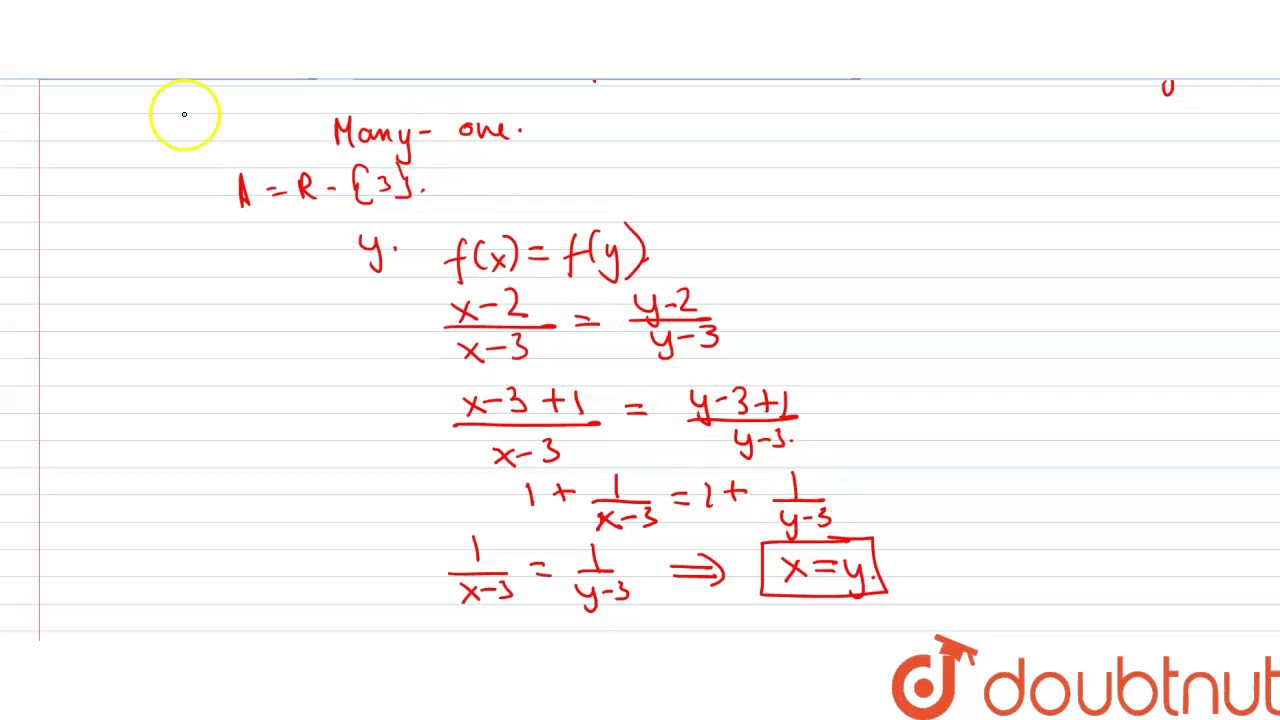
उदाहरण माना कि, हमारे पास निम्न है, (x 1)(x 2) विस्तार निम्न होगी ⇒(x 1)(x 2) = x 2 2x x 2 = x 2 (21) x 2 ∴ दूसरे पद का गुणांक = Proving it OnetoOne I understand a function f ( x) is onetoone if for x 1, x 2 ∈ I R, if f ( x 1) = f ( x 2) implies x 1 = x 2 The problem is when I set f ( x 1) = f ( x 2) this, I eventually get to x 1 3 x 1 3 = x 2 3 x 2 3 It's at this point I'm stuck, and don't know how to Justify your answer f (x) = ( (x − 2)/ (x − 3)) Check oneone f (x1) = ( (x"1 " − 2)/ (x"1" − 3)) f (x2) = ( (x"2 " − 2)/ (x"2" − 3)) Putting f (x1) = f (x2) ( (x"1 " − 2)/ (x"1" − 3)) = ( (x"2 " − 2)/ (x"2" − 3)) Rough Oneone Steps 1 Calculate f (x1) 2 Calculate f (x2) 3




Exercise Pdf Pdf Function Mathematics Trigonometric Functions



1 Show That The Function F R R Defined By F X 2x 3 Is One One And Onto Find F 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music



Www Assignmentexpert Com Homework Answers Math Answer Pdf




If F 1 0 E 5 Defined By F X E X 3 3x 2 Is One One Onto Many One Onto One One Into Many One Into Give Answer With Explanation Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
Is y=x^3x a onetoone function?To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW If` 2f(x)3f(1/x)=x^21` then `f(x)` isIt has been provided or mentioned that a function F(x1)=x^2–3x2 Interestingly, if we substitute a value of x1 in the place of x, we obtain, F((x1)1)=F(x) Therefore, F(x)=(x1)^2–3(x1)2=x^2–2x1–3x32=x^2–5x6 Hence, the function F(x) can




Show That The Function F R R Defined By F X 2x 1 3 Is One One And Onto Also Find The Inverse Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com
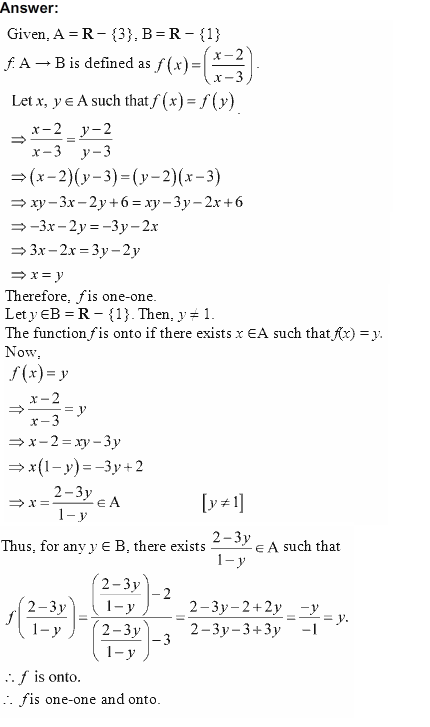



Ncert Solutions For Class 9 10 11 And 12 Let A R 3 And B R 1 Consider The Function F A B Defined By F X Is F One One And Onto Justify Your Answer
The graph of #f(x) = 2x^24x1# is a parabola with vertex #(1, 3)# (Use the vertex formula or put the expression in vertex form #f(x) = 2(x1)^2 3#) So with no restriction on the domain, the graph looks like graph{2x^24x1 697, 1081, 569, 32}Definition OnetoOne (Injection) A function f A → B is said to be onetoone if f(x1) = f(x2) ⇒ x1 = x2 for all elements x1, x2 ∈ A A onetoone function is also called an injection, and we call a function injective if it is onetoone A function that is not onetoone is referred to as manytoone ⇒ x = y So, f is oneone Surjectivity When x = 1 x 2 x 1 = 1 1 1 = 3 ⇒ x x 1 ≥ 3, for every x in N ⇒ f(x) will not assume the values 1 and 2 Therefore, f is not onto




State Whether The Function F R R Defined By F X 1 X 2 Is One One Onto Or Bijective




Ex 1 2 10 F X X 2 X 3 Is F One One Onto Class 12
That tells us that F of X is going to be equal to negative the anti derivative of one over X is actually going to be the natural log of the absolute value of X So then based on that, what we end up having is um plus C X Class D Um And the reason why we have plus six is because this is some constant> Assuming that the domain of x is R, the function is Bijective > ie it is both injective and surjective Lets see how 1 Checking for injection Injection means that the function is OneOne Let f(x1) = f(x2) => 2X1 1 = 2X2 2 => X1 = X2 Ex 13, 6 Show that f −1, 1 → R, given by f (x) = 𝑥/ (𝑥 2) is oneone Find the inverse of the function f −1, 1 → Range f (Hint For y ∈ Range f, y = f (x) = 𝑥/ (𝑥 2) , for some x in −1, 1, ie, x = 2𝑦/ (1 − 𝑦) ) f (x) = x/ (x2) Check oneone f (x1) = 𝑥1/ (𝑥1 2) f (x2) = 𝑥2/ (𝑥2 2) Rough Oneone Steps 1




Exercise 1 4 Types Of Functions Problem Questions With Answer Solution Mathematics




Show That The Function F In A R 23 Defined As F X 4x 36x 4 Is One One And Onto Hence Find F 1
∴ 5 x 1 = 5 x 2 ⇒ x 1 = x 2 ∴ f is oneone ie injective f is not onto ie surjective as for 1 ∈ N, there docs not exist any in N such that f (x) = 5 x = 1 0 ViewsIf f be a function such that f 9 = 9 f ' 9 = 3 then is If f is derivable at x = 1 then is equal to f a a f a f is continuous but not differentiable at x = 0 f is diSimple and best practice solution for f(x)=x^31 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it



2



2
• f(x) = x2 is not 1to1 • f(x) = x3 is 1to1 • f(x) = 1 x is 1to1 • f(x) = xn −x, n > 0, is not 1to1 Proof • f(x 1) = f(x 2) ⇒ 3x 1 − 5 = 3x 2 − 5 ⇒ x 1 = x 2 In general, f(x) = ax−b, a 6= 0, is 1to1 • f(1) = (1) 2= 1 = (−1) = f(−1) In general, f(x) = xn, n even, is not 1to1 • f(x 1) = f(x 2) ⇒ x3 = x3 2 ⇒ x 1 = x 2To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW If `f(x)=(x1)/(x1)` then `f(2x)` is equal toSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




Relations And Functions Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Toppers Bulletin




Relations And Functions Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Toppers Bulletin
Simple and best practice solution for F(x)=(x1)(x3) equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve itIn mathematics, a function (or map) f from a set X to a set Y is a rule which assigns to each element x of X a unique element y of Y, the value of f at x, such that the following conditions are met 1) For every x in X there is exactly one y in Y, the value of f at x;Then f(x) is not onetoone The reason f(x) would not be onetoone is that the graph would contain two points that have the same second coordinate – for example, (2,3) and (4,3) That would mean that f(2) and f(4) both equal 3, and onetoone functions can't assign two dierent objects in the domain to the same object of the target If




Ex 1 2 7 I In Each Of The Following Cases State Whether The




Answered X 2 Let F X And G X X 2 X Bartleby
M 2, and M 3 be metric spaces Let gbe a uniformly continuous function from M (with more than one point) onto itself 1 Solution Suppose for a contradiction that fThat is, f(x 1) = f(x 2) implies x 1 = x 2 In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of at most one element of its domain The term onetoone function must not be confused with onetoone correspondence thatWe start with a formal definition of a onetoone function Definition 11 Let f X → Y be a function We say f is onetoone, or injective, if and only if for all x1,x2 ∈ X, if f(x1) = f(x2) then x1 = x2 Or equivalently, if x1 6= x2, then f(x1) 6= f(x2) Symbolically, f X → Y is injective ⇐⇒ ∀x1,x2 ∈ X,f(x1) = f(x2) → x1 = x2
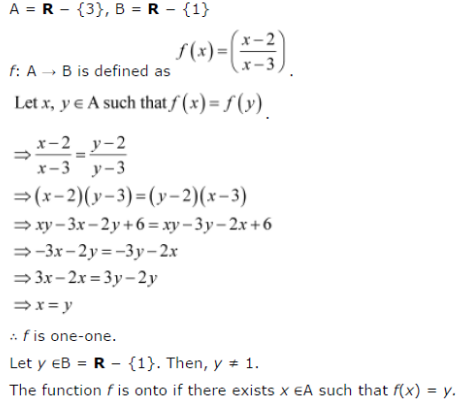



Let A R 3 And B R 1 Consider The Function F A B Defined By B Defined By Cbse Class 12 Maths Learn Cbse Forum




01 A I Is The Function F R R Defined By Y Chegg Com
1 Example 1 f(x) = x We'll find the derivative of the function f(x) = x1 To do this we will use the formula f (x) = lim f(x 0 0) Δx→0 Δx Graphically, we will be finding the slope of the tangent line at at an arbitrary point (x 0, 1 x 1 0) on the graph of y = x (The graph of y = x 1 is a hyperbola in the same way that the graph of2) If x and y are in X, then f (x) = y;




Pdf 01 Sets Relations And Functions Himanshu Gautam Academia Edu



2



1




The Function F 0 3 To 1 29 Defined By F X 2x 3 15x 2 36x 1 Is Youtube




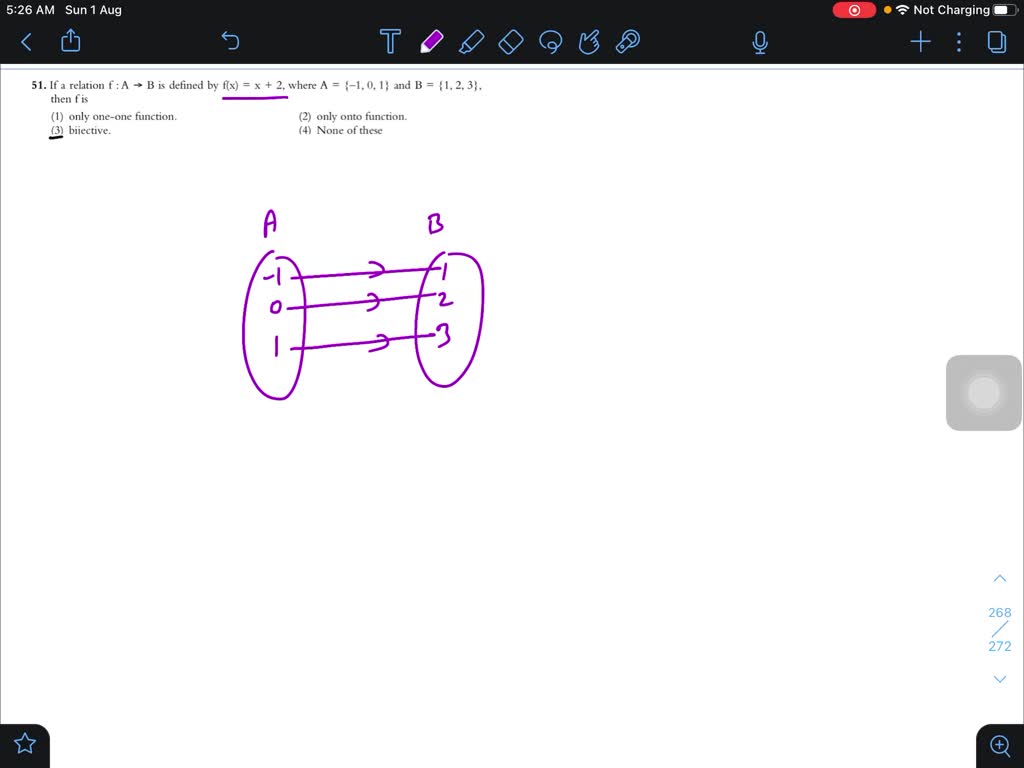
Mcs 013 Discrete Mathematics Block 1 By Ignou Mca Issuu



Anujitspenjoymath Files Wordpress Com 18 04 Csir Net Dec 17 Solution Pdf




Misc 4 Show F X X 1 X Is One One Onto Miscellaneous




Show That Function F R X In R 1 X 1 Defined By F X X 1 X X In R Is One One And Onto Function
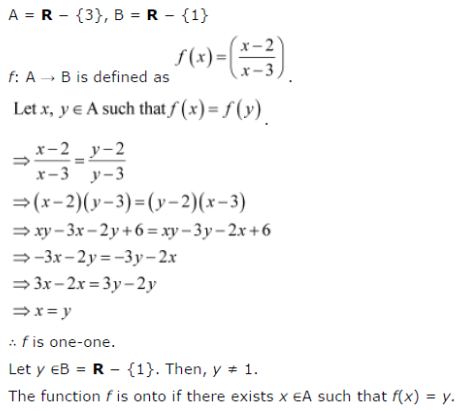



Let A R 3 And B R 1 Consider The Function F A B Defined By Cbse Class 12 Maths Learn Cbse Forum




Class Xii Maths Unit Relations And Functions




2 12 F R 3 2 R 10 X 1 3 2x G R 21 R 1o G X 1 X 2 H R 4 3 R 1 3 H X F O G X Verify If H X Is One To One And Onto If It Is Find The Inverse



Http Faculty Up Edu Wootton Discrete Section7 2 Pdf




The Function F 0 3 1 29 Defined By F X 2x3 15x2 36x 1 Is 12 A One One And Onto B Onto But Not One One C One One But Not Onto D Neither One One Nor Onto Snapsolve




Ncert Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Relations And Functions Avail Free Pdf




11 Discrete Structures Discrete Structures Unit 5 Ssk3003 Dr Ali Mamat Ppt Download




Relations And Functions Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Toppers Bulletin




Ppt Basic Structures Sets Functions Sequences And Sums Powerpoint Presentation Id



2




Determine If The Following Functions Are One To One Chegg Com




Final Relation1 M Tech Cse



Http Library Abes Ac In E Books Engineering mathematics iii module 4 2 Pdf




In Each Of The Following Cases State Whether The Function Is One One Onto Or Bijective Justify Your Answer Cbse Class 12 Maths Learn Cbse Forum




Let A R 3 And B R 1 Dot Consider The Function F Avecb Defined By F X X 2 X 3 Dot Show That F Is One One And Onto And Hence Find F 1



Let A R 3 B R 1 And F A Rarr B Defined By F X X 2 X 3 Is F Bijective Youtube




Check The Following Functions For One One And Onto A F R Rarr R F X 2x 3 7 B F R Rarr R F X X 1 C F R 2 Rarr R F X 3x 1 X 2 D F R 1 1 F X Sin 2 X



2




Ex 1 2 10 F X X 2 X 3 Is F One One Onto Class 12



Let A R 3 And B R 1 Consider The Function F A B Defined By F X X 2 X 3 Show That F Is One One And Onto And Hence Find F 1




Exercise 5 Let F R 1 To R 1 Be The Function De Gauthmath



Sol 10 Prove That The Function F Rr F X X2 X Is Math



One To One Function Explanation Examples




12 Onto State Whether The Function F Is Bijective Just Math




The Function F R R Defined By F X X 1 X 2 X 3 Is A One One But Not Onto B Onto But Not One One C Both One One And Onto D Neither One One Nor Onto




For Real X Let F X X 3 5x 1 Then 1 F Is Oneone But Not Onto R 2 F Is Onto R But Not Oneone 3 F Is Oneone And Onto R 4 F




In Each Of The Following Cases State Whether The Function Is One One Onto Or Bijective Justify Your Answer I F R R Defined By F X 3 4x Ii F




The Function F R R Defined By F X X 1 X 2 X




6 A Let F R R Be The Function Defined By F X Chegg Com



Let A R 3 And B R 1 Consider The Function F A B Defined By F X X 2 X 3 Show That F Is One One And Onto And Hence Find F 1



2




If A Function F 2 Oo R Defined By F X X 1 X 2 X 3 Is




Show That Function F In A R 2 3 Defined As F X 4x 3 6x 4 Is One One And Onto Hence Find F 1 Mention Each And Every Formula And Minute Details Mathematics Topperlearning Com W22iulbb




Show That F R R Is Given By F X 1 X Is Neither One One Nor Onto Brainly In




Define A Function F R Rightarrow R By Is F Chegg Com



Jwr6i3cpy 9iem




Example 9 Prove That F X 2x Is One One And Onto Chapter 1




Mathematics Session Set Relation Function Session Ppt Download




Final Relation1 M Tech Cse




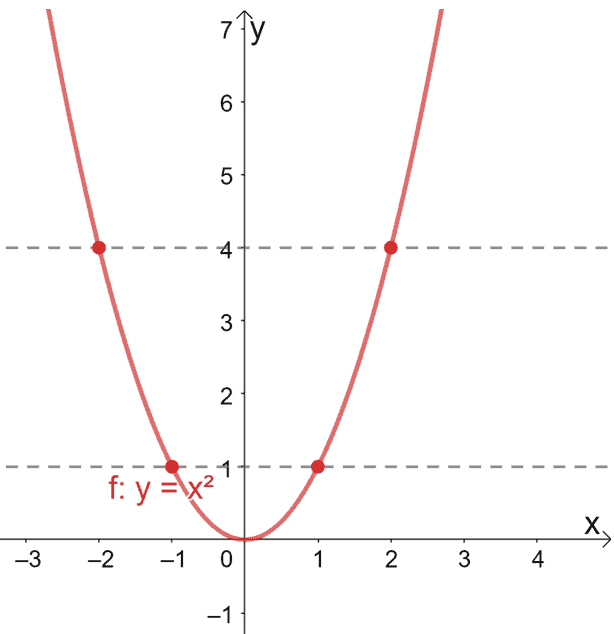
Example 11 Show F X X2 Is Neither One One Nor Onto Examples




Cs 2 Discrete Structures And Their Applications Functions




Misc 5 Show F X X3 Is Injective Chapter 1 Class 12 Cbse




Discrete Maths Hw3 Solutions




Ex 1 2 10 F X X 2 X 3 Is F One One Onto Class 12




Example 11 Show F X X2 Is Neither One One Nor Onto Examples




Relations And Functions Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Toppers Bulletin




Ex 1 2 10 F X X 2 X 3 Is F One One Onto Class 12




1 A Let A W X Y Z B 1 2 3 4 5 C Chegg Com




If The Function F R 1 1 To A Definded By F X X 2 1 X 2 Is Surjective Youtube




Example 12 Show That F X X 1 If X Is Odd X 1 If X Is Even




Show That The Function F R R Defined By F X 3x 3 5 For All X In R Is A Bijection Youtube




For The Functions Below Show If The Function Is Chegg Com




Let F R R Be A Function Defined By F X X 3 X 2 3x Sin X The Function Is Onto Or Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class Ncert Solutions




11 Discrete Structures Discrete Structures Unit 5 Ssk3003 Dr Ali Mamat Ppt Download



Show That The Function F In A R 2 3 Defined As F X 4x 3 6x 4 Is One One And Onto Hence Find F 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Answered 1 Let F R R Be Defined By F X 2x Bartleby




Let F X 2x 3 X 3 If Function F One One And Onto Is F




F Z Z Given By F X X2 4 Is This Function One One And Onto Mathematics Topperlearning Com Ysr2iwzz




Please Show Work And Answer Full Question This Js Discrete Math 1 Determine Whether Each Of The Functions Homeworklib
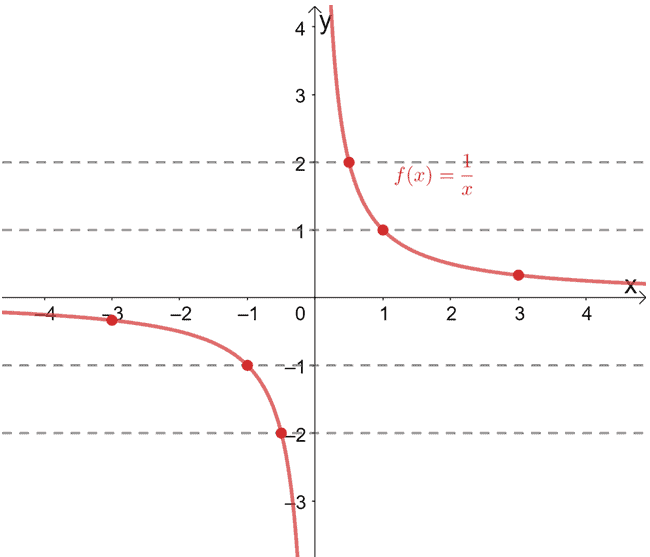



One To One Function Explanation Examples




8 10 Points Consider Functions F G H Defined Chegg Com




Ethiopia Learning Math Grade 11 Page 930 In English



2



1




Could Someone Help With Problem 3 Ive Tried X1 X2 But No Matter What I Can T Seem To Get The Answer Askmath




Prove That The Function F R Rightarrow R Given By Chegg Com




12 Onto State Whether The Function F Is Bijective Just Math




The Function F R R F X X 1 X 2 X 3 Check If It Is One One On Askiitians



Q Tbn And9gcsmm4ktmxrxm10kmsg3wqo5rzire Ogwbm0v2tajixhbesgniod Usqp Cau



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿